Evidence to support Virtual Reality in Medical Education — A Paradigm Shift with HoloMedicine® Spaces
For decades, medical students have relied on textbooks, 2D scans, and static anatomical models. While these tools have their merits, they struggle to convey the spatial complexities and dynamic nature of human anatomy, especially in surgical specialties. Understanding intricate anatomical relationships and pathologies in the context of the human body requires a three-dimensional perspective that traditional tools often fail to provide.
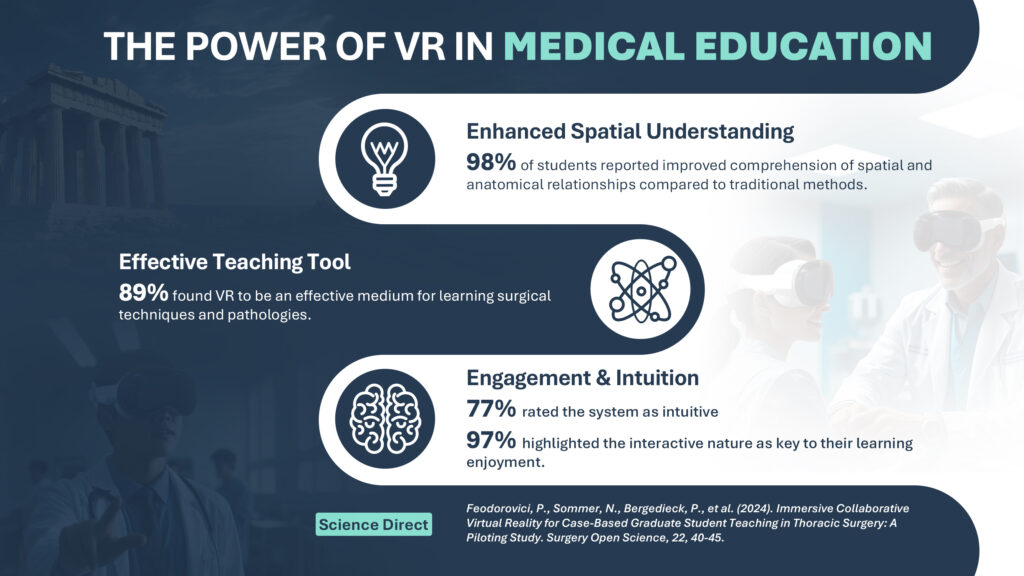
Studies like the one published by Feodorovici et al. (2024) demonstrate the limitations of traditional methods and emphasize the transformative potential of VR in overcoming these barriers ([1] Feodorovici, P., Sommer, N., Bergedieck, P., et al. (2024). Immersive Collaborative Virtual Reality for Case-Based Graduate Student Teaching in Thoracic Surgery: A Piloting Study. Surgery Open Science, 22, 40-45). As surgical pathologies often involve dynamic and spatially complex elements, VR offers a unique way to visualize and understand these intricacies.
Studies with VR systems allowing students to interact with real-time, three-dimensional CT imaging of thoracic surgical cases showed the following:
An astonishing 98% of students reported improved comprehension of spatial and anatomical relationships compared to traditional methods.
Nearly 89% found VR to be an effective teaching medium for surgical techniques and pathologies.
With a user-friendly design, 77% rated the system as intuitive, and 97% highlighted the interactive nature as a key factor in their enjoyment of learning.
Only 5.7% experienced cyber sickness, underscoring the system’s accessibility.
The findings of this study underscore VR’s role as a powerful teaching tool that seamlessly integrates theoretical and practical knowledge in medical education.
An astonishing 98% of students reported improved comprehension of spatial and anatomical relationships compared to traditional methods.
Nearly 89% found VR to be an effective teaching medium for surgical techniques and pathologies.
With a user-friendly design, 77% rated the system as intuitive, and 97% highlighted the interactive nature as a key factor in their enjoyment of learning.
Only 5.7% experienced cyber sickness, underscoring the system’s accessibility.
The findings of this study underscore VR’s role as a powerful teaching tool that seamlessly integrates theoretical and practical knowledge in medical education.
HoloMedicine® Spaces represent the pinnacle of VR innovation for medical education. Unlike conventional setups, HoloMedicine® is designed for scalability, collaboration, and adaptability—qualities essential for modern teaching:
1. Real-Time Collaboration
HoloMedicine® enables multiple users, from students to instructors, to interact within a shared virtual space. This fosters teamwork and simulates real-world clinical environments, regardless of physical location.
2. Detailed Visualization
Using real patient imaging data, HoloMedicine® offers lifelike 3D representations of anatomical structures. This clarity allows educators to demonstrate variations and pathologies that traditional methods cannot replicate.
3. Flexibility and Accessibility
HoloMedicine® Spaces can be deployed across campuses or accessed remotely, making them ideal for institutions aiming to expand their reach without compromising educational quality.
Platforms like HoloMedicine® play a pivotal role in addressing these challenges by offering intuitive, immersive solutions for diverse educational needs.
Medical educators can leverage HoloMedicine® Spaces to integrate VR seamlessly into curricula. Case-based learning becomes more interactive and impactful as students not only observe but manipulate and explore anatomical models. The platform also supports asynchronous learning, enabling students to revisit VR sessions at their convenience—a feature particularly valuable for complex surgical topics.
As highlighted in the journal, transitioning from traditional cadaver-based dissection to virtual anatomy models not only reduces costs but also addresses ethical and logistical challenges. Moreover, the enhanced interactivity of VR tools ensures that students gain a more profound and engaging learning experience.
The applications of VR extend beyond thoracic surgery. Fields like orthopedics, neurology, and cardiology stand to benefit immensely from immersive, 3D learning environments. Studies suggest that platforms like HoloMedicine® Spaces could also be adapted for interdisciplinary learning, combining medical training with engineering or technological innovation.
The flexibility of VR also allows for global collaboration. By connecting students and educators worldwide in shared virtual spaces, VR fosters an inclusive learning ecosystem that transcends geographical limitations. These platforms offer scalability and adaptability for a broad range of medical applications, ensuring that both under-resourced and advanced institutions can benefit from the technology.
While the potential of VR in medical education is immense, its implementation is not without challenges. Issues such as cost, technological infrastructure, and resistance to change in traditional teaching methods must be addressed. However, the study conducted by Feodorovici et al. provides a roadmap for overcoming these obstacles, emphasizing the importance of early adoption and comprehensive training programs for educators and students alike.
Future advancements in VR technology, such as higher-resolution displays and more intuitive interfaces, promise to further enhance the user experience. Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence with VR platforms could provide personalized learning experiences, adapting content to the needs of individual students.
The evidence is clear: VR is more than a novelty in medical education. It is a necessity. Platforms like HoloMedicine® Spaces provide the infrastructure to make this vision a reality. As educators, embracing this technology is not just about keeping pace with innovation—it’s about empowering the next generation of medical professionals with tools that enhance understanding, foster collaboration, and ultimately save lives.
Institutions must invest in VR infrastructure and training programs to ensure widespread adoption. Early adoption efforts require careful planning but yield significant benefits, including improved student engagement, reduced resource dependence, and enhanced learning outcomes.
The integration of VR into medical education marks the dawn of a new era. HoloMedicine® Spaces, with their robust features and transformative potential, are poised to lead this revolution. By adopting these advancements, institutions can ensure that future doctors are equipped with the skills and knowledge they need to excel in an increasingly complex healthcare landscape.